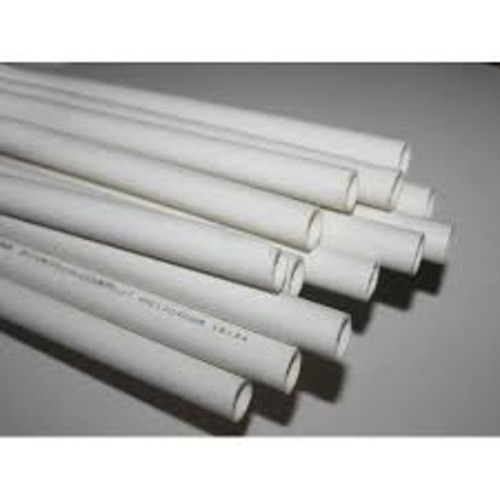
PVC Conduit
22 INR/Meter
Product Details:
X
PVC Conduit Price And Quantity
- 22 INR/Meter
- 22.00 - 140.00 INR/Meter
- 1000 Meter
PVC Conduit Trade Information
- Vadodara
- Cash Advance (CA) Cash in Advance (CID) Cheque
- 10000 Meter Per Month
- 3 Days
- Standard Packaging
- All India
Product Description
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) conduit is a type of electrical conduit made from PVC material, which is widely used for protecting and routing electrical wiring in both residential and commercial buildings. It is a highly durable, flexible, and cost-effective option for wiring systems. A PVC conduit typically contains the following components and features:
PVC Conduit Manufacturer in India
PVC Conduit Manufacturer in Gujarat
PVC Conduit Manufacturer in Vadodara
PVC Conduit Supplier in India
PVC Conduit Supplier in Gujarat
PVC Conduit Supplier in Vadodara
1. PVC Material
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) is the primary material used to manufacture the conduit. PVC is a thermoplastic material that is resistant to corrosion, moisture, chemicals, and UV light, making it suitable for both indoor and outdoor applications.
- The PVC used is non-conductive, providing electrical safety by preventing accidental electric shocks.
2. Conduit Wall
- Thickness and Strength: PVC conduit typically has a thick, rigid wall structure that provides durability and protection to the cables inside. The thickness can vary, with schedule 40 being the most commonly used for general-purpose applications and schedule 80 providing thicker walls for heavy-duty or high-impact applications.
- The thickness of the conduit™s wall helps to ensure that it can withstand external pressure, mechanical damage, and environmental factors.
3. Surface Finish
- The surface of PVC conduits is usually smooth, allowing for easy pulling of wires inside and reducing the risk of wear and tear. The smooth surface also prevents dust and debris buildup inside the conduit.
4. Flexibility (Flexible PVC Conduit)
- Some PVC conduits are flexible (referred to as flexible PVC conduit or spiral-wound conduit), which allows for easier installation in areas where rigid conduit is difficult to use.
- Flexible PVC conduits are typically used when the conduit needs to navigate corners or bend around obstacles.
5. Size and Diameter
- PVC conduit comes in a range of sizes, typically measured in diameters (in inches or millimeters). Common sizes include -inch, -inch, 1-inch, 1-inch, and 2-inch.
- The diameter of the conduit depends on the number of cables to be routed through it, with larger diameters used for higher numbers of cables or larger cable sizes.
6. Color
- PVC conduits are usually available in gray or white colors, though some may come in other colors depending on the manufacturer and specific application.
- Gray PVC conduit is the most common for standard electrical installations, whereas white may be used in specific types of systems like low-voltage wiring.
7. End Caps and Fittings
- Connectors, Elbows, Tees, and Couplings: These fittings are used to join multiple lengths of PVC conduit together, make turns, or branch out the conduit system.
- End Caps: These are used to seal the open ends of the conduit to prevent dust, moisture, or insects from entering the system.
- Adapters: PVC conduit may require adapters when transitioning between different types of conduit (e.g., from PVC to metal conduit).
8. Joints and Couplings
- PVC conduit can be connected using solvent cement or compression fittings. Solvent cement (also known as glue) chemically bonds the pieces together, providing a waterproof and secure connection.
- Compression fittings are used when joints need to be disassembled or adjusted without permanent bonding.
9. UV Resistance (for Outdoor Use)
- Some types of PVC conduit are designed to be UV-resistant, making them suitable for outdoor installations. These UV-resistant conduits are usually made with special additives to prevent degradation when exposed to sunlight.
10. Reinforced PVC Conduit (For Heavy-Duty Use)
- For more demanding applications (such as industrial or underground installations), PVC conduit may be reinforced with additional materials like fiberglass or metal. This makes it more impact-resistant and durable under harsh conditions.
11. Electrical Safety and Compliance
- PVC conduits are manufactured to meet safety standards and electrical codes (like IEC, UL, or BS standards), ensuring that they provide adequate protection to electrical wires from mechanical damage, heat, and fire.
- The conduit is non-conductive, which helps protect against short circuits or electric shocks.
12. Sizes and Types
- Rigid PVC Conduit: This is the most common type of conduit used for electrical wiring in buildings, offering a solid and reliable protection system.
- Flexible PVC Conduit: This is used where flexibility is required, such as in areas that need to be easily moved or reconfigured. Flexible PVC is often used for short runs or where flexibility is more important than mechanical strength.
- Schedule 40 and Schedule 80: These are the two most common types of rigid PVC conduits. Schedule 40 is standard for most residential and commercial applications, while Schedule 80 is used for areas that require more mechanical strength or protection.
13. Applications
- Indoor Wiring: PVC conduits are widely used in residential and commercial buildings to protect electrical wiring within walls, ceilings, and floors.
- Outdoor Installations: UV-resistant PVC conduits can be used outdoors or in direct sunlight.
- Underground Wiring: PVC is commonly used for underground electrical installations (though often in combination with a protective sleeve or in a more durable version like "heavy-wall" PVC).
- Industrial Use: In factories or industrial settings, more robust types of PVC conduit (like rigid heavy-duty PVC or reinforced varieties) are often used for protecting electrical cables from mechanical damage.
Advantages of PVC Conduit:
- Corrosion Resistance: PVC does not rust or corrode like metal conduits, making it ideal for use in damp or corrosive environments.
- Cost-Effective: PVC conduit is generally cheaper than metal alternatives like steel or aluminum.
- Easy to Install: It is lightweight, easy to cut, and requires no special tools or expertise for installation.
- Durable: Resistant to most chemicals, moisture, and UV light.
- Non-Conductive: Provides electrical insulation, making it safer for wiring installations.
Disadvantages:
- Not Suitable for High-Temperature Areas: PVC conduit is not as heat-resistant as some other materials, so it is not recommended for areas with high heat exposure (e.g., near heaters or in industrial furnaces).
- Brittle in Extreme Cold: It can become brittle and more prone to cracking in extremely low temperatures.
Enter Buying Requirement Details





 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send SMS
Send SMS